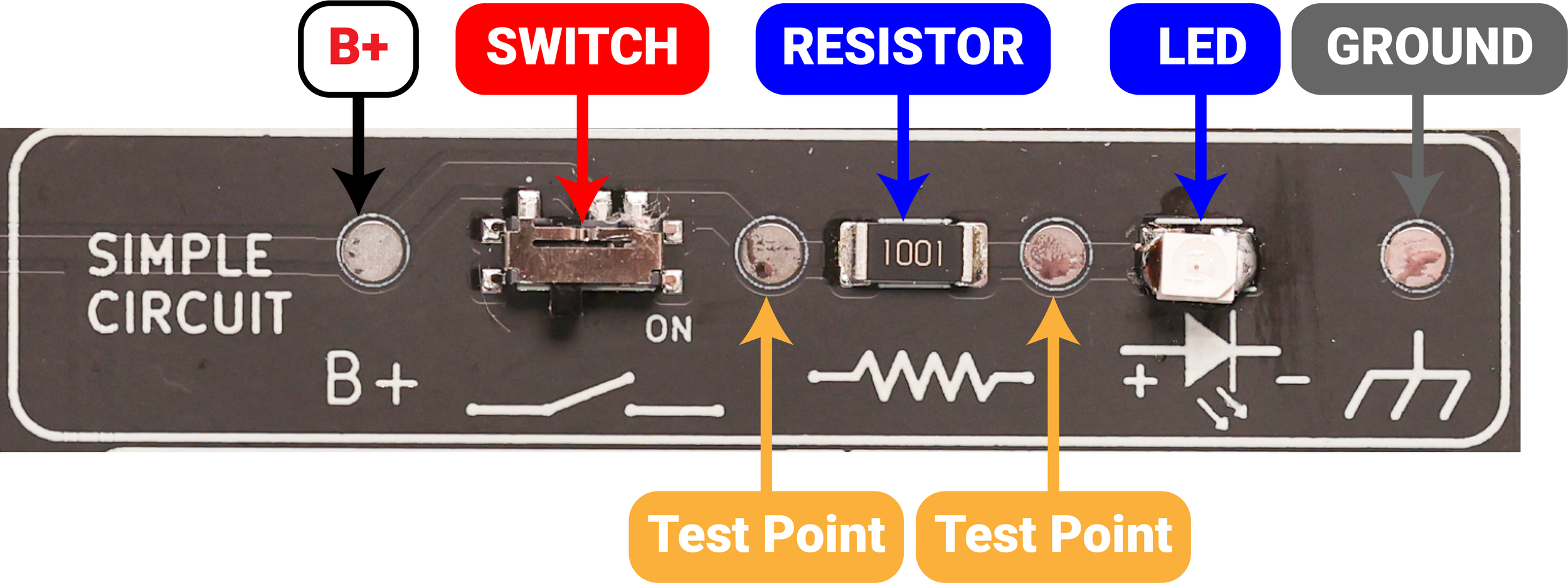
Here’s the path the current takes:
B+ Test Point – This is the positive power source. It represents the battery’s positive terminal.
Switch – The sliding switch controls whether current can flow. When it’s turned on (to the right), the circuit is complete, and power can move through the rest of the components.
Resistor – The resistor limits the amount of current flowing through the circuit. This protects the LED from too much current and demonstrates how resistance affects voltage drop.
LED (Light Emitting Diode) – The LED lights up when current flows through it in the correct direction. This shows that LEDs only conduct one way and helps visualize current flow.
Ground (GND) – The ground point completes the circuit, returning current to the negative side of the power source — just like the chassis ground in a vehicle.
You’ll notice test points placed between each component.
These are used to take voltage measurements with a multimeter so you can see how voltage changes as it moves through the circuit.